Economic trees, found in urban areas, hold more than just ornamental value. They contribute significantly to both local communities and the global economy. These trees bear fruits, provide valuable timber, and play a vital role in environmental preservation. In this article, we will delve into the utilization and significance of economic trees, emphasizing their pivotal role in sustainable development. We’ll explore specific examples, the benefits they offer, and the challenges they face in today’s world, such as deforestation and climate change.
Versatile Utilizations of Economic Trees:
Timber Production: One of the primary uses of economic trees is for timber production. Trees like oak, teak, and mahogany are highly sought after for their quality wood, which is used in construction, furniture making, and various industries.
Fruit Trees: Trees like apples, mangoes, walnuts, and cashews are cultivated for their edible fruits and nuts. These provide essential nutrition and income for communities, contributing to food security and livelihoods.
Medicinal Properties: Many trees have medicinal properties. For instance, the bark of the cinchona tree is a source of quinine, used to treat malaria. The Neem tree is known for its antifungal and antibacterial properties.
Oilseed Trees: Trees like the oil palm and coconut trees are cultivated for their oil-rich fruits. These oils have various industrial applications and are used in cooking, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
Environmental Benefits:
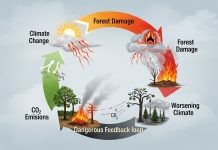
Carbon absorption: Economic trees are vital in mitigating climate change. They absorb and store carbon dioxide, helping to reduce greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere.
Biodiversity Conservation: These trees provide home and food sources for a diverse range of wildlife, supporting ecosystems and biodiversity.
Economic Significance:
Employment Generation: The cultivation and harvesting of economic trees create jobs for millions of people globally, particularly in rural areas.
Income Generation: Through the sale of timber, fruits, nuts, and other products, economic trees contribute significantly to the income of individuals and communities.
Challenges and Conservation:
Deforestation: Cutting down trees and using land in an unsustainable way is a danger to many valuable economic tree species. Efforts to combat deforestation and promote sustainable forestry are crucial.
Pest and Disease Management: Economic trees are vulnerable to various pests and diseases. Research and management strategies are essential to protect tree populations.
So in summary, economic trees are an integral part of our global ecosystem, providing a wide array of benefits from economic prosperity to environmental sustainability. Recognizing their significance and implementing sustainable practices in their cultivation and management is essential for a balanced and thriving future.